Torus Palatinus
What is Torus Palatinus?
It is a condition wherein there is a bony outgrowth at the roof of the mouth (palate). The protrusion arises on the midline at the roof of the mouth (palate). It affects not only humans but other mammalian organisms too.
What does palatinus mean? It is derived from a Latin word “torus” meaning lump and “palatinus” meaning palate. In other words, a torus palatinus is a lump on the palate. The palate is one of the most important parts of the mouth. It splits the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
Torus palatinus comes in various shapes such as a nodule, lobular, spindle-like, and irregular shapes. (1, 2, 3)
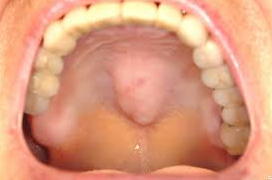
Picture 1: An image showing a lump on the palate.
Image Source: www.dhinfo.org

Picture 2: A severe case of torus palatinus that warrant surgical removal.
Photo Source: diseasedefinition.info
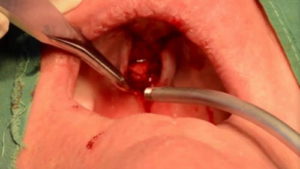
Picture 3: A surgical removal of a bony outgrowth on the palate.
Image Source: i.ytimg.com
Torus palatinus types
- Flat tori – It has a flat appearance that originates from the midline of the palate. The base is broad and smooth. The size grows bigger as it expands symmetrically to both sides.
- Spindle tori – The outgrowth looks like a slender shaped rod with tapered ends.
- Nodular tori – The tori looks like small nodules and each nodule has its own base. In a severe condition, the nodules combine to make a large nodular growth.
- Lobular tori – it has a lobe-like structure sharing a common base and arises from the midline of the palate. (3, 4, 5)
Torus Palatinus Causes
- Heredity. Torus palatinus can be passed on through genes. If any of the parents have torus palatinus, there is a possibility that the offspring will have it too.
- Bruxism and clenching (excessive grinding of the teeth)
- Trauma to the bones of the oral cavity (injury)
- Forced mastication (chewing)
- Blockage in the salivary gland
- Nutrient deficiency
- Side effects of medications. Some drugs used to treat seizures and muscle spasms can cause torus palatinus. (4, 5, 7)
Prevalence rate
About 20% of the general population has torus palatinus. It occurs after the puberty period but is more prevalent in adults. Torus palatinus is common in women. (4, 6)
Is it contagious?
Torus palatinus is not contagious. In fact, it is not a disease condition but more of a clinical manifestation of a health condition. The catch is that it is not infectious. (2, 4)
Torus palatinus Symptoms
As mentioned above, torus palatinus is not a disease. It is an abnormal anatomical condition wherein the tissue surrounding the palate becomes bony. There is no definite signs and symptoms. The patient will usually feel an unusual growth at the roof of the palate. The abnormal growth starts from a small nodule and will then transition into a big colossal bump.
Some people experienced difficulty in swallowing and drinking. The severe type can cause damage to the surrounding tissues of the oral cavity. In rare instances, the overgrowth can cause infection that may spread to other parts of the oral cavity, which includes the palate and the bone. When this happens, the patient will complain of torus palatinus pain. (6, 7, 8, 9)
Differential Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s clinical manifestations. The doctor will check for the presence of distinct massive tissue outgrowth.
In most instances, the patient needs to be examined by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. When deemed necessary, more laboratory tests and biopsy are ordered. (1, 3)
Treatment and Management
Treatment might not be necessary because the outgrowth seems to be normal. In the event that the torus palatinus causes discomfort and further problem to the patient, then it should be surgically removed.
Torus palatinus should be surgically removed if:
- It becomes too large that it creates irritation.
- It causes discomfort when brushing the teeth.
- The patient is unable to eat and drink well.
- If the outgrowth causes problems in wearing dentures.
Torus palatinus removal can be performed under local and general anesthesia. Torus palatinus surgery is performed by a maxillofacial surgeon. To begin with, the surgeon will stain the site to make it more visible. The target area will be incised to expose the tissues underneath.
The torus palatinus will be gently and carefully removed. The prognosis is good. There are some postop complications but are minimal such as swelling and bleeding. Infection is extremely rare. In just a few weeks, the patient will be back to the usual self. (2, 5, 7, 8, 9)
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torus_palatinus
- http://healthfixit.com/torus-palatinus/
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/torus-palatinus
- http://diseasedefinition.info/torus-palatinus-definition-symptoms-causes-treatments-pictures/
- https://www.dhinfo.org/2017/06/torus-palatinus-what-is-causes-symptoms-and-treatment/
- http://www.ghorayeb.com/TorusPalatinus.html
- https://healthool.com/torus-palatinus/
- https://emedicalhealth.net/torus-palatinus/#.WjFi5fCWbIU
- https://www.justanswer.com/topics-torus-palatinus/
